The transition to the Agentic Enterprise represents the most significant architectural shift since the dawn of the cloud. It promises unprecedented levels of productivity and automation, but it also introduces profound challenges that relate to governance, security, and operational complexity. Using a piecemeal approach - deploying agents in silos without a unifying strategy - is a direct path to technical debt and organizational chaos.
Deploying agents without a central management plane creates significant operational risk, including security vulnerabilities from direct system access, lack of observability into agent interactions and actions, and high costs due to redundant point-to-point integrations. This siloed deployment strategy results in a brittle environment that’s difficult to manage at scale. A sustainable model requires a unified platform for agent integration and governance.
MuleSoft provides a comprehensive, unified, and open platform to confidently guide enterprises throughout their journey. It leverages the enterprise’s existing API landscape as the foundation for agentic actions, and accelerates creation of new agent-ready assets through a trusted, AI-powered development lifecycle. Through enterprise-grade support for open standards like Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Agent2Agent (A2A) protocols, it makes these assets actionable for both simple commands and complex multi-agent collaboration, regardless of how the AI landscape evolves. MuleSoft Agent Fabric provides a solution to discover, orchestrate, govern, and observe the entire agent ecosystem. Through this integrated approach, MuleSoft Agent Fabric provides a proven foundation to scale a network of trusted AI agents, which transforms the promise of AI into tangible, automated business outcomes and realizes the full potential of the intelligent enterprise.
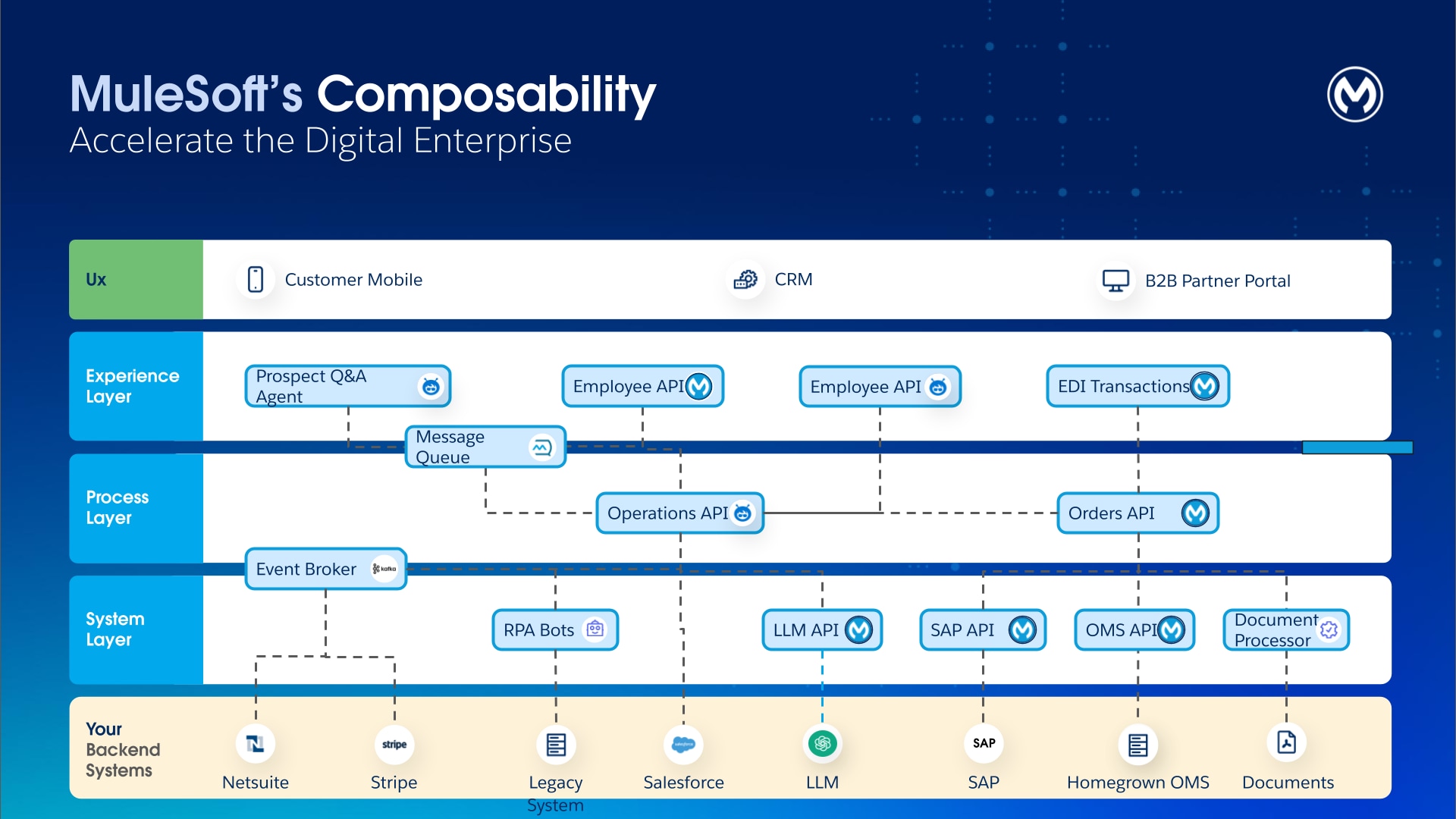
The established three-layered approach of API-led connectivity - System, Process, and Experience APIs - provides a powerful framework for structuring agent actionability.
- System APIs offer a consistent, secure, and abstracted interface to underlying systems of record. They decouple agents from the complexity of backend protocols and data models, which ensures that all agent actions are performed on governed, reliable endpoints.
- Process APIs encapsulate complex, multi-step business logic. Agents don’t need to understand the intricate orchestration that’s behind creating sales orders, checking inventory, or initiating shipments. They can use Process APIs (for example, "Process Order") without having to handle the underlying complexities. Process APIs provide a safe, transactional, and auditable mechanism for agents to execute business processes, which dramatically reduces the agent reasoning required and ensures that business rules are consistently enforced.
- Experience APIs were traditionally designed to serve specific UI applications (for example, Order Management App); however, they can also be repurposed as context-rich actions for agents. This provides agents with essential information to perform a given task without requiring multiple calls to downstream systems.
To meet the rising demand for agent-ready tools and capabilities, enterprises must accelerate the development of the APIs and integrations that form the composable foundation. MuleSoft addresses this challenge by embedding generative AI directly into the development lifecycle, which creates a virtuous cycle that uses AI to build the high-quality assets that other agents consume.
For developers, MuleSoft Vibes acts as an intelligent partner by automating the most repetitive aspects of integration development and providing a unified, agentic interface for the entire software development lifecycle. Through MuleSoft Vibes in Anypoint Code Builder, developers interact with generative capabilities that are powered by the trusted Einstein AI Pipelines, which makes the AI-assisted development process smooth and efficient. This pipeline - the Inference Graph Execution Service (IGES) - is a multi-stage process that’s used to achieve high-quality results. It consists of grounding, validation, error correction, and rigorous evaluation.
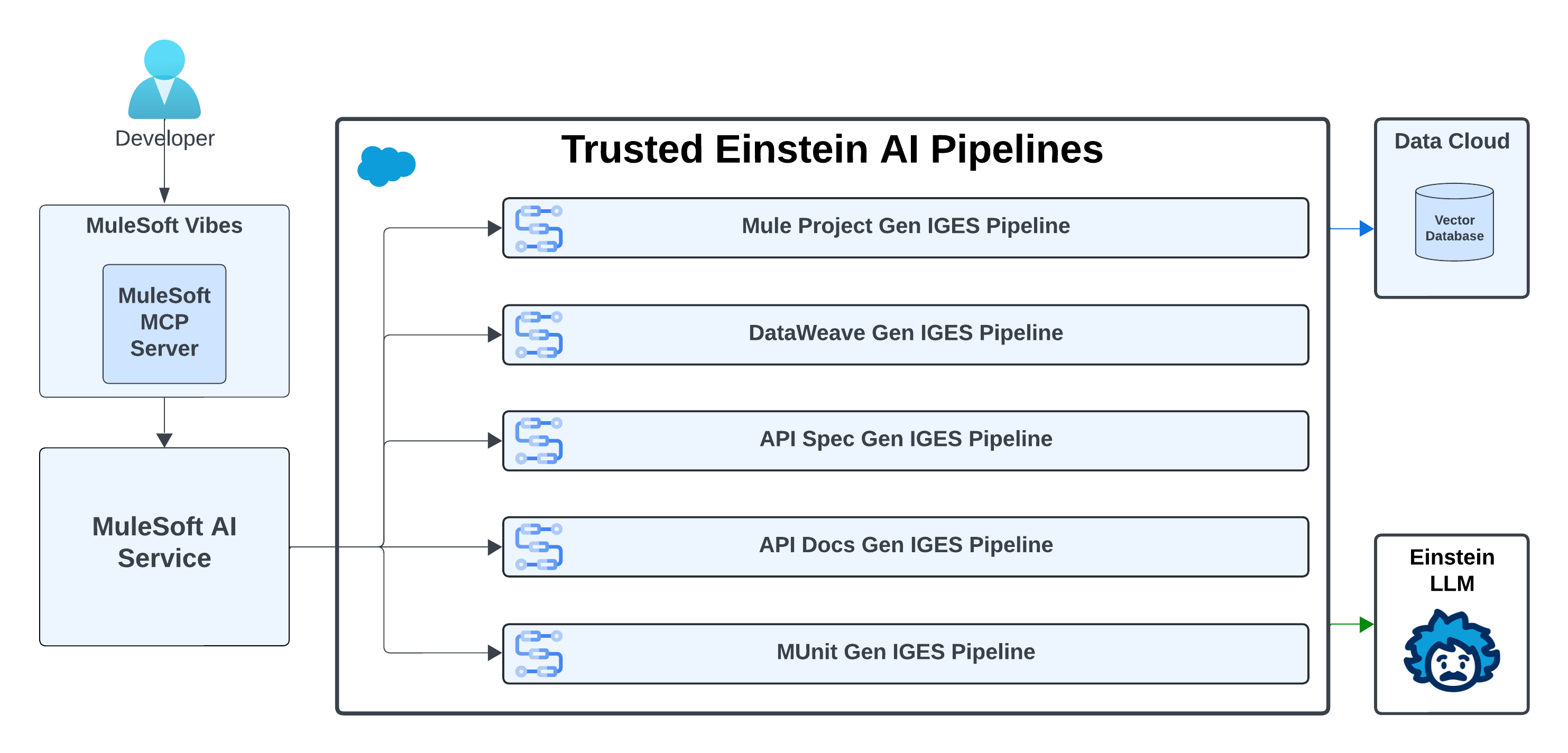
- Generative Flows capability in MuleSoft Vibes is built on the Agentforce AI framework. It transforms natural language business logic (User Prompts) into functional Mule applications. The IGES Pipeline consists of following steps:
- Conversation History Summarization: The LLM analyzes the current prompt and the user’s prior messages to create a summarized prompt that captures user intent and conversation history. This consolidated prompt improves the accuracy of subsequent data retrieval and generation steps.
- Flow Semantic Retrieval from a Vector Database: The system takes the summarized prompt from the previous step and performs a semantic search against a vector database that contains 200+ connectors, 7,000+ connector operations, and 7,000+ sample code snippets. It retrieves the most relevant connectors, operations, and code examples to ground the generation process using accurate data and ensures that outputs are aligned with MuleSoft’s extensive connector ecosystem. Since MuleSoft is the industry standard for connectors and operations, this grounding provides the model with rich context and domain accuracy that generic LLMs lack.
- Augmentation: The retrieved content and conversation history messages are then combined with the summarized prompt. This augmented prompt guides the LLM to reduce hallucinations. It also includes instructions to prevent the generation of toxic content.
- Flow Generation: This step leverages the Einstein AI LLM model to generate raw XML code that’s based on the context and examples that are provided. This is the core step of the generation pipeline.
- Post-processing and Validation: The post-processor and validator checks the code to ensure correct syntax and the use of valid connector operations while a separate toxicity check flags harmful content.
- Multi-Step Error Correction: If all of the initial generations are invalid, the automated error correction mechanism analyzes the error messages to detect patterns. Then, it resubmits the prompt to the LLM along with enriched error messages and corrective metadata.
- Config File Generation: This step extracts relevant connector metadata, augments the prompt, and sends it to the LLM to generate accurate connector configurations. Lastly, all POM and XML namespaces are generated deterministically using the latest version of each dependency, which eliminates hallucinations and ensures consistency.
- DataWeave Transformation Generation: Data transformation is often the most time-consuming part of integration development. MuleSoft Vibes tackles this process using the multi-step approach that’s similar to the Mule Flow XML generation.
- Intention Reasoning: The LLM analyzes user input and output data samples to infer and articulate high-level transformation logic in natural language. This step separates the user's goal from the literal data values that may have been provided in the prompt.
- DataWeave Semantic Retrieval: To find the most semantically relevant DataWeave function documentation and complete transformation examples, the system uses the generated prompt from the previous step as a query to the vector database. This grounds the generation process in high-quality, verified information.
- Augmentation: The retrieved functions and examples are combined with the original user prompt to create a context-aware set of instructions for the subsequent LLM call, which influences the LLM's behavior to reduce hallucinations.
- DataWeave Generation: This step leverages the LLM model to generate a DataWeave transformation script and an accompanying explanation that’s based on the provided context and examples. This is the core step of the generation pipeline.
- Post-processing and Validation The generated script is evaluated against two specific metrics: validity and correctness. The script must compile without syntax errors (validity) and produce the expected output when it’s run using the sample input (correctness).
- Multi-Step Error Correction: If the initial validation fails, then this plugin identifies the error categories and corrects the issues in the generated script. This refinement helps improve the overall success rate and accuracy of the system.
- Final Post-processing and Validation The corrected script from the error-correction module undergoes a re-validation process to ensure that it’s syntactically valid and functionally correct. This final quality gate ensures that the output is accurate and reliable before sending it back to the user.
- API Specification and Documentation Generation: Developers can generate fully-validated OpenAPI (OAS) or RAML specifications by describing the desired API in natural language. MuleSoft Vibes ingests the prompt (which includes details on resources, methods, security schemes, and parameters) and produces a valid, syntactically correct API definition. After generation, it can create documentation for the API in Anypoint Exchange, which covers everything from authentication to endpoint details and error handling, freeing developers from these types of tedious tasks.
- AI-Assisted MUnit Generation: Quality assurance is paramount for assets that are consumed by autonomous agents. MuleSoft Vibes helps generate MUnit test cases directly from the Mule Flow Code. This helps to mock external dependencies and assertions, and identify common testing gaps, which drastically reduces the manual effort that’s required to achieve high test coverage and ensure the reliability of the integration logic.
Developers thrive in their preferred environments. That’s why MuleSoft meets developers where they are, which allows them to build integrations in their AI IDE of choice. MuleSoft’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) Server exposes development, deployment, and management capabilities as MCP Tools that any VS Code-based AI-native IDE (for example, Cursor, Windsurf, or Trae) can consume to interact with the Anypoint Platform using natural language.
By packaging its core IDE functionality into a standard VS Code extension, MuleSoft decouples its tools from a branded IDE shell, which enables development tooling to be IDE agnostic. Instead of competing with the fast-paced evolution of IDEs, this architecture choice allows MuleSoft’s development tools to stay compatible and accessible across the growing ecosystem of modern, AI-powered IDEs.
In an Agentic Enterprise, having a robust foundation of composable APIs is necessary, but insufficient. The next critical step is to ensure that these assets are discoverable, understandable, and invocable by AI agents. This requires an "actionability layer" that’s built on open standards that are designed specifically for agentic communication. MuleSoft provides enterprise-grade tooling for the two dominant emerging protocols:
- MCP for agent-to-system interactions
- A2A for agent-to-agent interactions
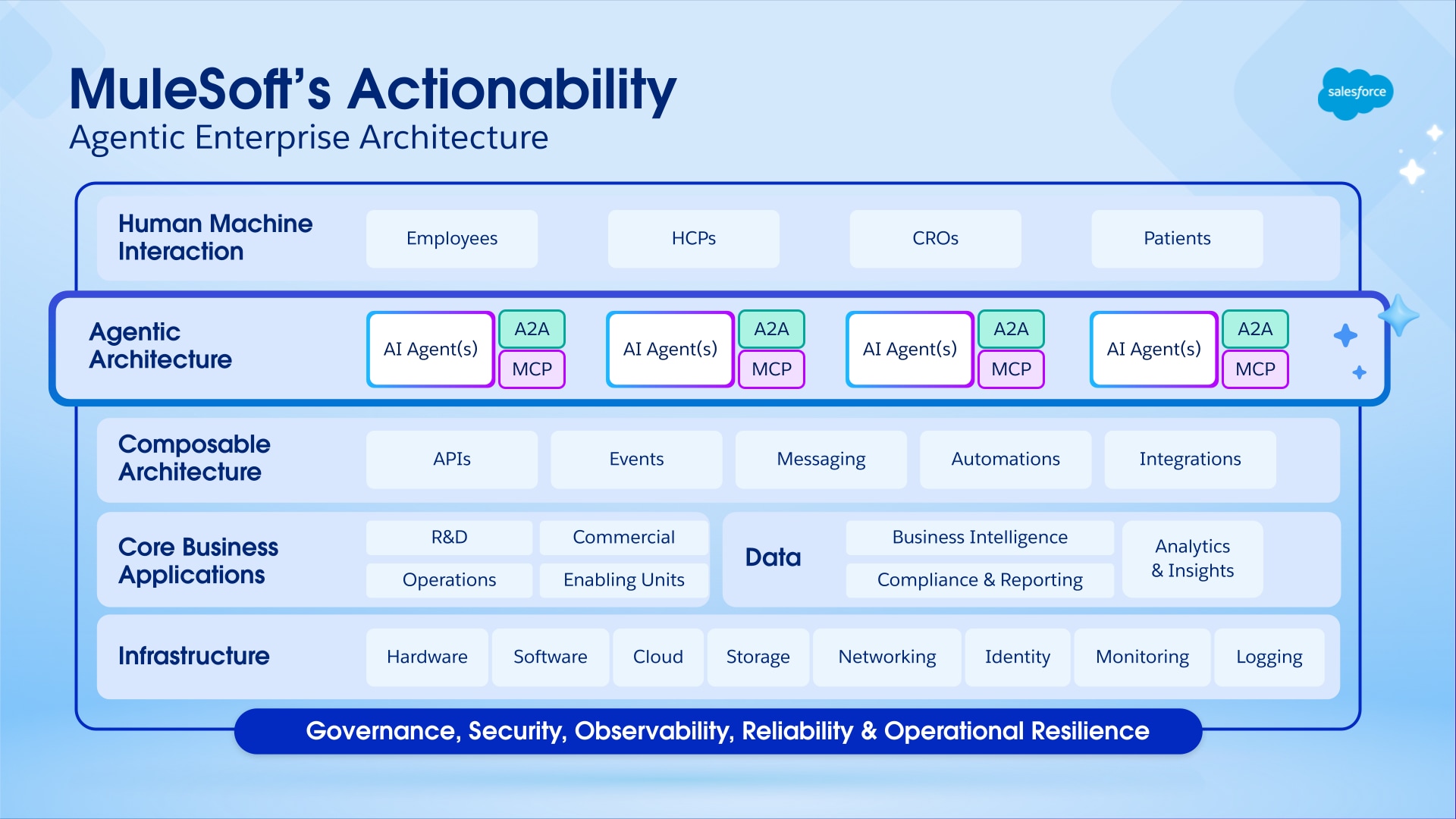
MCP has rapidly emerged as the industry standard for agent-to-tool communication, which is analogous to what REST became for web services. MCP allows AI agents to dynamically discover a system's capabilities, understand its inputs and outputs, and invoke it to perform an action, all without requiring pre-programmed or hard-coded logic.
The MuleSoft MCP Connector allows any API that’s implemented as a Mule application to be published as an MCP server. Since MuleSoft provides hundreds of pre-built connectors to virtually every major enterprise system (for example, SaaS, legacy, and databases), this instantly transforms an organization's APIs and applications into a set of agent-ready tools. An API that’s designed to check inventory in SAP, a flow that processes a new lead in Salesforce, or a custom application that’s connected via MuleSoft can all be made available to AI agents as atomic, governed tools using the MCP Connector.
While the MCP excels at hierarchical, agent-invoking-tool interactions, complex business processes often require collaboration between multiple specialized agents. The Agent-to-Agent (A2A) protocol is the emerging open standard that’s designed to facilitate peer-to-peer communication that enables sophisticated, multi-agent workflows.
MuleSoft's support for A2A allows enterprises to design and build advanced systems with the same level of governance and reliability that they expect for their APIs. The MuleSoft A2A Connector allows developers to easily expose any agent as an A2A server, or invoke any A2A compliant agent from a Mule application. For example, a mortgage application process may be orchestrated across a "Credit Check Agent," a "Document Signature Agent," and a "Regulatory Compliance Agent," with each agent discovering and invoking the others' capabilities (as needed) to move the application forward.
By providing robust, enterprise-grade tooling for MCP and A2A, MuleSoft supports building a flexible ecosystem that consists of direct agent-to-system interactions (via MCP tools) and agent-to-agent (A2A) interactions. Regardless of how the AI landscape evolves, this approach positions MuleSoft as the underlying foundation that connects all forms of agentic communication.
As enterprises adopt agentic AI, they inevitably face the challenge of agent sprawl. To prevent this from devolving into chaos, a dedicated orchestration layer is required. MuleSoft Agent Fabric (demo) is a comprehensive architectural solution that’s designed to address this challenge head-on. It provides a central management plane to discover, govern, orchestrate, and observe the entire network of AI agents, regardless of where they’re built or how they operate. Functioning as the "air traffic controller" for the enterprise's digital workforce, MuleSoft Agent Fabric transforms a collection of fragmented, siloed agents into a cohesive, secure, and high-performing intelligence network.
MuleSoft Agent Fabric is built upon four integrated pillars that cover the complete lifecycle management for agents as first-class enterprise assets.
The foundation of any managed ecosystem is discoverability. The Agent Registry serves as the universal, centralized catalog for every agentic asset within the enterprise. This includes custom-built agents, agents that are embedded in SaaS applications, MCP servers that expose legacy systems, and A2A endpoints for inter-agent collaboration. By providing a single source of truth, the Agent Registry solves the critical discovery problem by preventing teams from building redundant capabilities, and enabling human developers and other AI agents to dynamically find and reuse existing assets at scale.
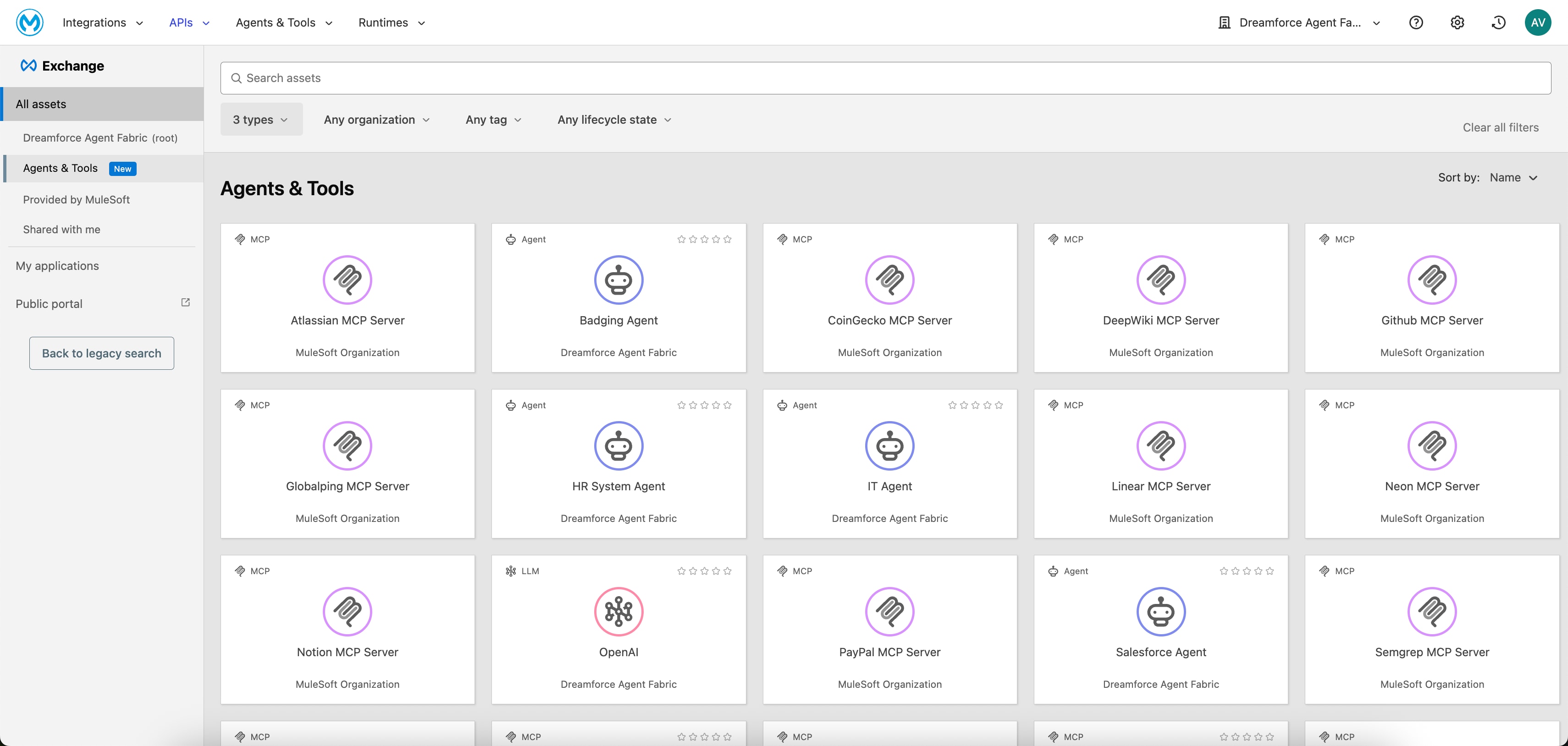
The Agent Registry is built upon Anypoint Exchange, and it adds three new asset types: Agents, MCP Servers, and LLMs. It captures information about these assets, including MCP tools, transport protocols, and agent cards, as well as the dependencies between agents and the MCP servers and tools that they consume. Developers can create and manage assets directly within the registry. They can also programmatically discover and reuse existing assets within MuleSoft Vibes (via the MuleSoft MCP Server’s search_asset tool) when creating new orchestrations. This equips developers with all of the information they need to understand and consume these assets.
Once assets are discoverable, they must be orchestrated to perform useful work. The Agent Broker is an orchestration service that executes multi-step business processes. It uses a configurable LLM to interpret high-level tasks and generate corresponding workflows. The Agent Broker dynamically discovers, sequences, and invokes the required agents and tools to complete these processes.
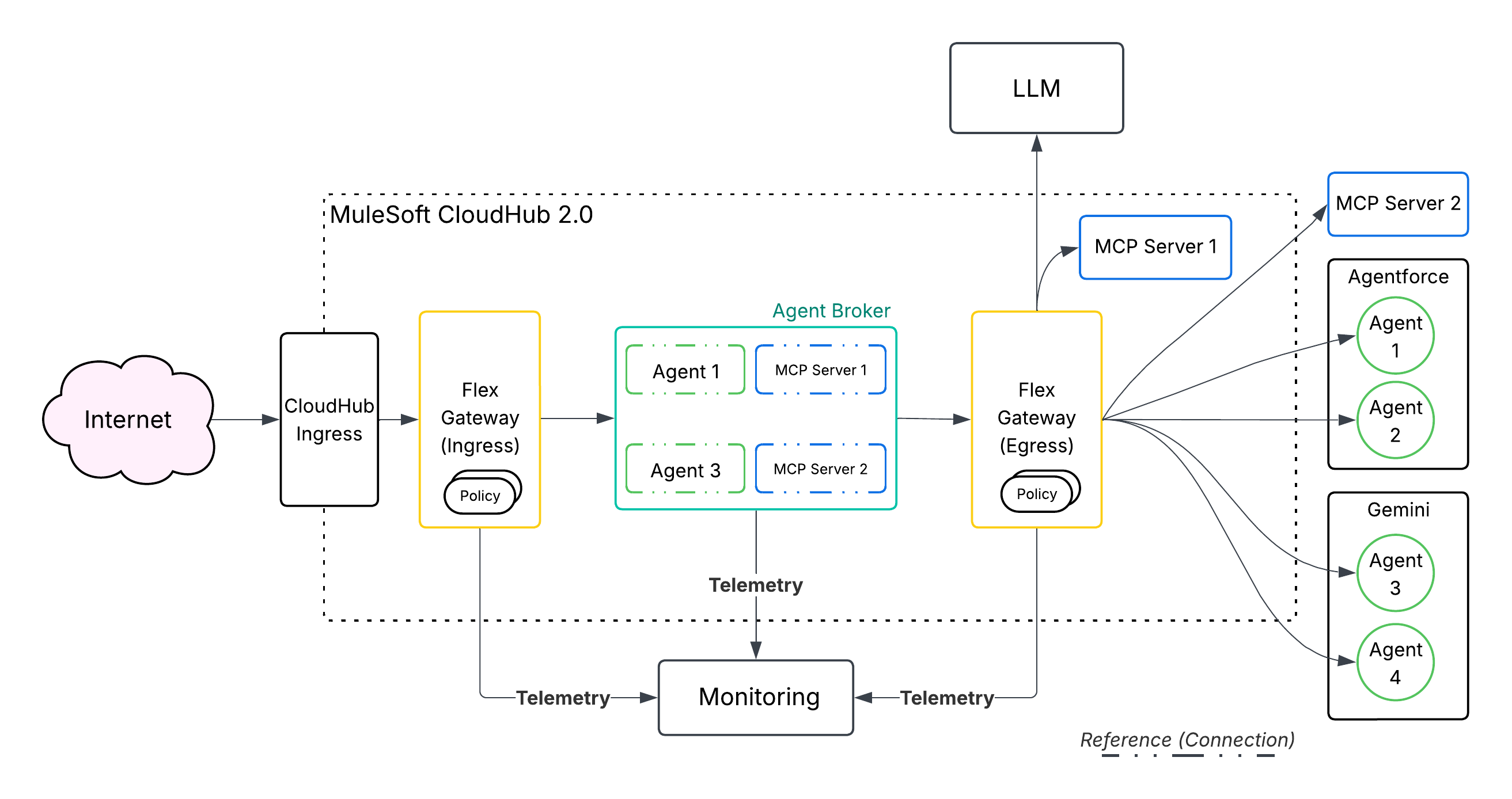
Connectivity is managed via the MCP for tools and an A2A protocol for agents. This allows the system to organize agents into business-specific domains (for example, Supply Chain or Finance) and route tasks across all of them. A single, natural-language prompt (for example, ”Onboard an Employee.”) is decomposed into a sequence of discrete actions that are executed by different agents or tools across multiple backend systems. Agent Broker Orchestration includes:
- Dynamic Orchestration Pattern: This is an Agent-Loop pattern that determines sub-tasks and orchestrates them across the most suitable agents and tools to achieve the overall goal. By leveraging this pattern, collaborative agents can be built to solve complex use cases (for example, handling a complex service escalation).
- LLM-Powered Reasoning: Uses an LLM to interpret natural language goals and generate execution plans, which removes the need for hard-coded, rigid workflow logic.
- Configurable LLM Model: Allows developers to specify which LLM model to use, which provides control over cost, performance, and capabilities.
- Natural Language Development: Agent Broker logic can be defined using natural language via MuleSoft Vibes.
- Observability: Anypoint Monitoring provides logging and tracing upon deployment to help users understand and debug Agent Broker’s reasoning and interactions with MCP tools and A2A Agents.
- Managed Deployment: Agent Broker is a containerized application that’s backed by Mule Runtime, which manages availability and scalability of the deployment.
The Anypoint Flex Gateway is the mechanism through which certain policies are technically enforced. MuleSoft Agent Fabric leverages the Anypoint Flex Gateway to secure, inspect, and manage every agentic interaction that happens via MCP and A2A protocols. This allows organizations to apply a rich set of enterprise-grade policies to all agentic traffic to ensure that every action is secure, compliant, and auditable prior to its execution. To safely and responsibly scale AI adoption, these guardrails are critical.
| Policy Name | Protocol(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| JWT Validation Policy/Client ID Enforcement Policy | A2A, MCP | The JWT Validation Policy/Client ID Enforcement Policy secures A2A agents and MCP servers by restricting access to authenticated callers only. |
| Schema Validation | A2A, MCP | Schema Validation ensures that incoming agent requests conform to the A2A or MCP specification, which prevents malformed traffic. |
| A2A PII Detector | A2A | A2A PII Detector identifies Personally Identifiable Information (PII) in requests and responses, and enables logging or blocking to meet compliance requirements. |
| A2A Prompt Decorator | A2A | A2A Prompt Decorator injects custom context or instructions into prompts that are sent to agents to guide their behavior and enforce guardrails. |
| MCP Attribute-Based Access Control | MCP | MCP Attribute-Based Access Control regulates access to specific tools and resources that are exposed by an MCP server based on user attributes (for example, Tiers, IP, or JWT claims). |
| SSE Logging | A2A, MCP | SSE Logging records the content of Server-Sent Events (SSE) streams that are used by agentic protocols for comprehensive auditing and traceability. |
| Rate Limiting and Spike Control | A2A, MCP | The Rate Limiting and Spike Control protects backend agents and systems from traffic surges and denial-of-service attacks by enforcing request limits. |
| A2A Agent Card | A2A | The A2A Agent Card rewrites the Agent Card URL to ensure that all traffic is correctly proxied through the governed Flex Gateway instance. |
Enterprise Governance Policies for Agentic Protocols
In addition to governing inbound requests, the Anypoint Flex Gateway also manages all outgoing connections and requests from an agent to external services (for example, MCP Servers and Tools or other agents). This includes:
- Logging: Provides a centralized observability point to monitor and log all outbound agent requests for auditing and troubleshooting.
- Security: Prevents sensitive data leakage by inspecting outbound traffic.
- Authentication: Manages credentials for external systems by applying outbound authentication mechanisms, including API Keys, OAuth, and ClientId/ClientSecret from a single point.
The Anypoint Flex Gateway Policy Development Kit (PDK) allows users to create custom policies when out-of-the-box policies don’t meet specific requirements. By using the PDK, developers can write policy logic in the Rust programming language and compile it into a WebAssembly (WASM) module. The self-contained module is then loaded into the Anypoint Flex Gateway to enforce unique security rules, custom data transformations, or specialized integration logic directly at the API edge. This provides a powerful, high-performance way to extend gateway functionality for unique or complex use cases.
Here are the four key components of the PDK:
- Anypoint CLI PDK Plugin: This plugin creates the PDK project and uploads the compiled policy to Exchange. It also generates a Makefile that simplifies the development process by providing a clear set of commands to build and manage the policy.
- Policy Template: When a new project is created, the PDK generates a basic scaffold or template. This structure includes all of the necessary files and configuration that are required to successfully compile the policy, which gives developers a starting point for custom logic.
- SDK Building Tools: These tools abstract the complex, event-driven architecture of the underlying Envoy proxy. By using reactor and executor patterns, the SDK provides a straightforward, linear coding method. This helps to reduce complexity, improve debugging, and lower the learning curve for developers.
- Policy Management: The MuleSoft MCP Server provides MCP tools to help users manage the custom policy lifecycle. Examples of these tools include:
- get_flex_gateway_policy_example
- manage_api_instance_policy
- manage_flex_gateway_policy_project
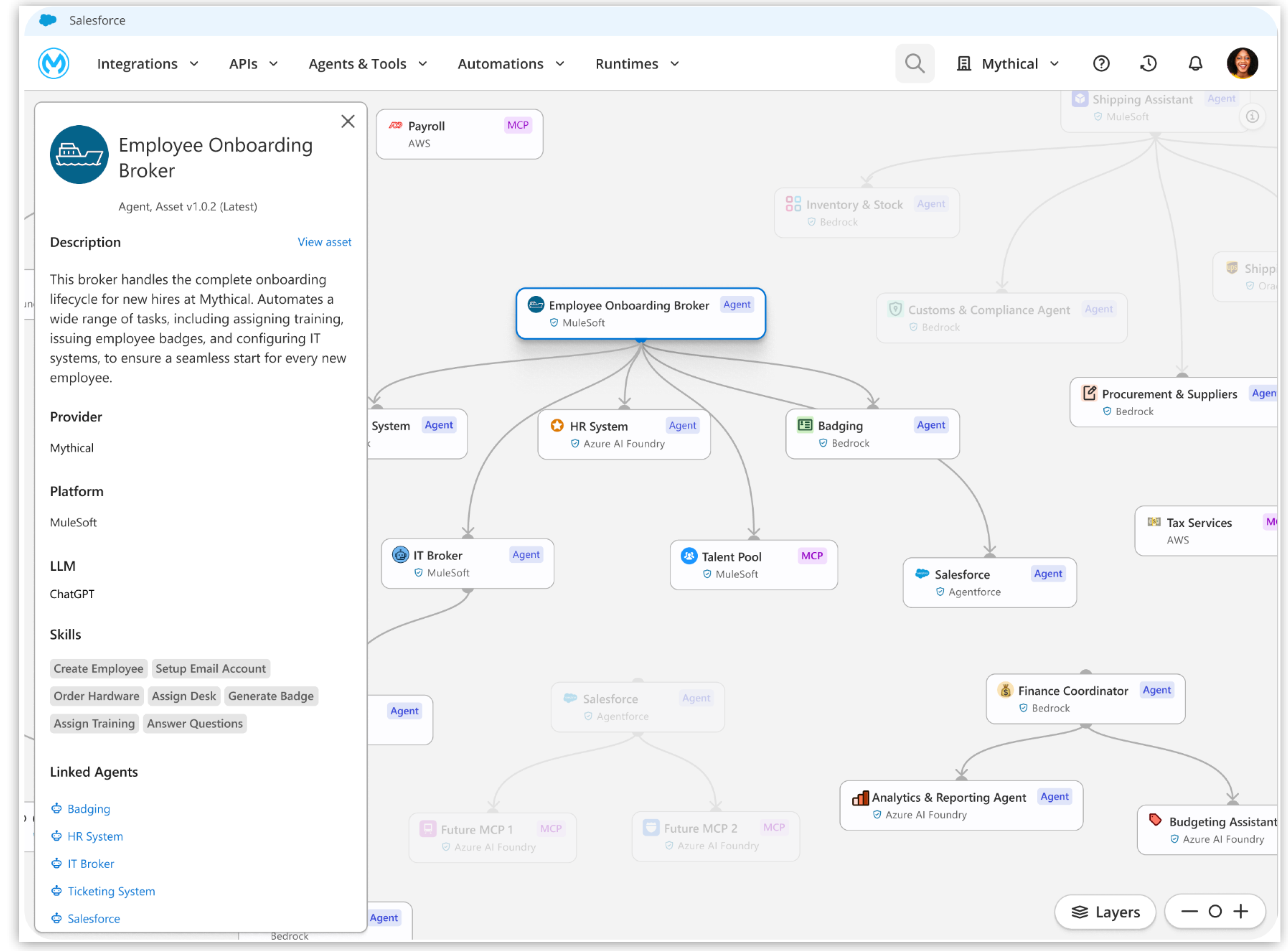
The Agent Visualizer provides a real-time, dynamic map of the entire agent network, turning what could be a "black box" of AI interactions into a fully-observable system. Architects and operations teams can use the Agent Visualizer to review how agents are connected, trace their decision flows, monitor their health and performance, and identify dependencies. This level of visibility is crucial to optimize performance, troubleshooting failures efficiently, detect bottlenecks, and build confidence in deployed agents.
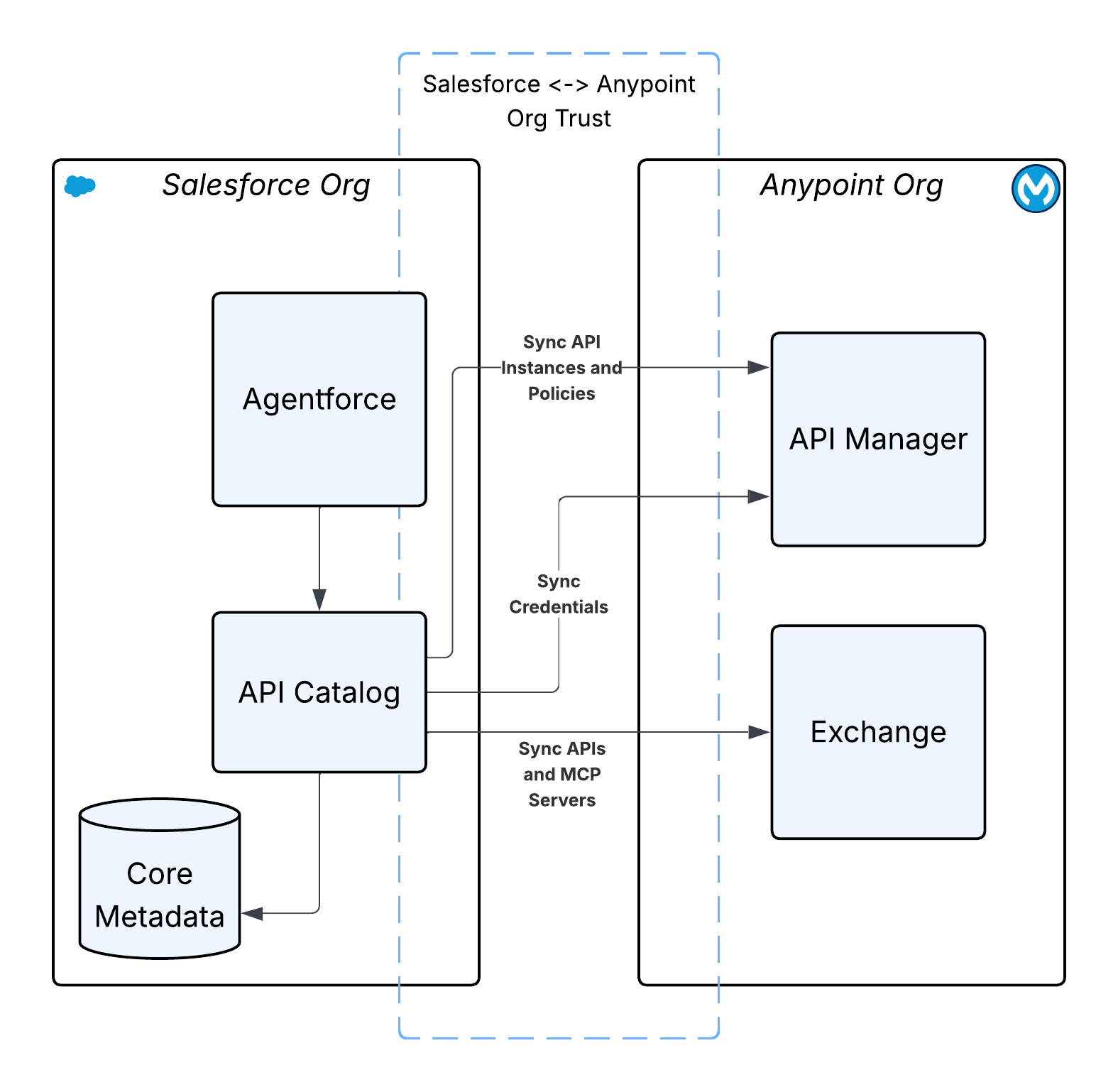
The MuleSoft API Catalog and Topic Center are designed to improve how APIs are discovered, used, and managed, particularly in conjunction with Agentforce.
All of the MuleSoft APIs that are designed and published can be made discoverable and consumable via the API Catalog in the Salesforce Platform. The API Catalog serves as the centralized repository, and it unifies all of an organization's APIs from MuleSoft, Salesforce, Heroku, and other clouds into a single view. This makes it easy for developers and administrators to discover, understand, and reuse existing APIs by enabling them to be used in automations (for example, Agentforce, Flow, and Apex).
The MuleSoft for Agentforce: Topic Center allows developers to structure their APIs around specific business use cases by defining Agentforce Topics and Actions metadata at design time itself. This includes:
- Actions, which are the tasks that an agent can perform
- Instructions, which guide the agent on how to apply certain actions
By adding this semantic layer, the Topic Center makes APIs understandable and consumable by Agentforce, which ensures that it can interact with enterprise systems effectively.
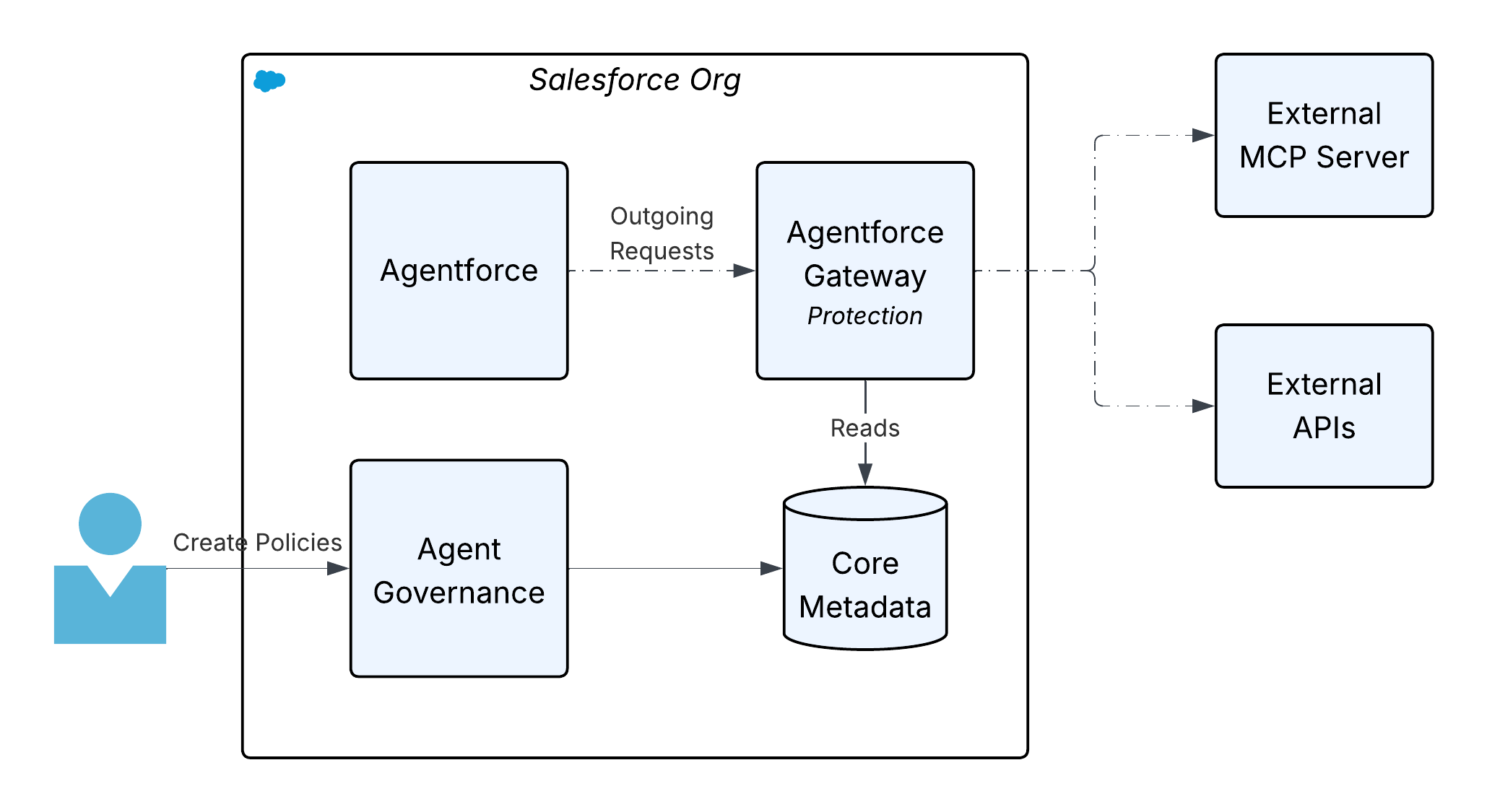
The Agentforce Gateway is a centralized governance layer that’s designed to manage and secure interactions within the expanding Agentforce ecosystem. As Agentforce integrates with additional third-party APIs and tools via protocols like MCP, the primary function of the Agentforce Gateway is to enforce policies (for example, rate limits and tool restrictions) on all outbound traffic that’s initiated by Agentforce, and audit all of the outgoing requests.
The Agentforce Gateway leverages the existing MuleSoft API governance policy engine, which is built natively into the Salesforce Platform. This Envoy-based policy engine intercepts agent traffic, applies configured policies (for example, attribute-based access control and quota limits), and manages authentication and authorization, all without requiring customers to install additional gateway infrastructure.
Deploying a governed network of agents is a landmark achievement. However, it introduces new "Day 2" operational challenges. It requires an enhanced level of operational intelligence to monitor, measure, and troubleshoot a dynamic, distributed system of autonomous actors. The ultimate architectural vision is a system where AI isn’t only used to execute business processes but also to monitor, manage, and heal the very infrastructure that it runs on.
MuleSoft’s vision for integration intelligence leverages the power of the broader Salesforce ecosystem to provide deep, customizable insights into the performance of the integration fabric and the agentic network. By capturing and storing OpenTelemetry (OTEL) compliant data - the emerging standard for observability - in Salesforce Data 360, organizations can create a unified repository for logs, metrics, and traces across their entire landscape. This data can be viewed in Tableau via pre-built dashboards and custom visualizations to gain detailed insights into API performance, agent interaction patterns, and overall system health.
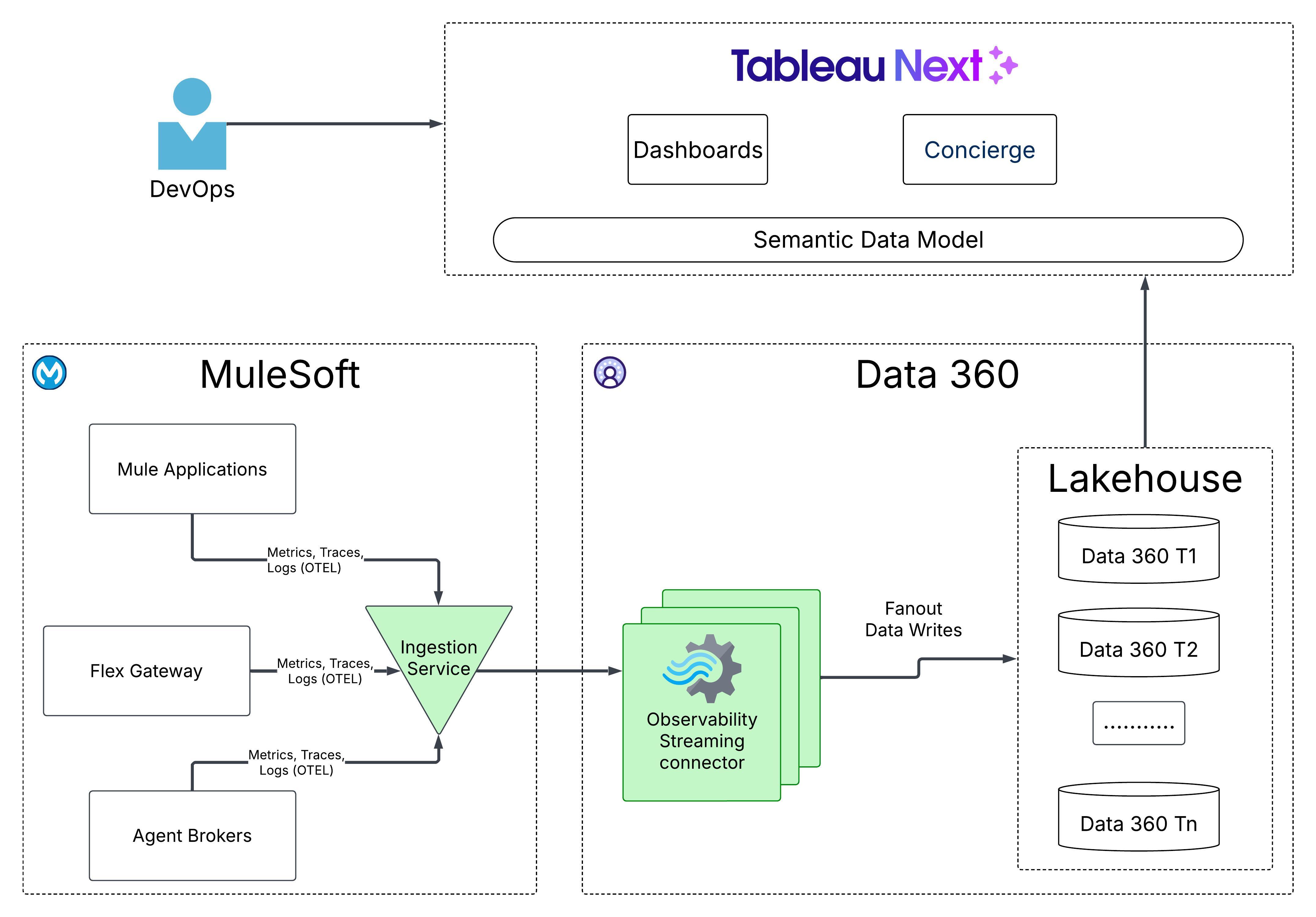
This system has three key components:
- Ingestion: The ingestion service is the centralized entry point for collecting and processing telemetry data from various Mule applications, Agent Brokers, and Flex Gateways. It performs schema validation, data normalization, and filtering to maintain data quality and consistency across various applications. In addition, it enforces controls (for example, authentication, encryption, tenant fairness, and rate limiting) in the ingestion pipeline.
- Storage: A high-throughput streaming job runs in Data 360 that reads data from multi-tenant Kafka topics, and transforms it into the OTEL format. OTEL data is then committed to the tenant’s Data 360 in the TelemetryTraceSpan, TelemetryLogs, and TelemetryMetrics DMOs in the Lakehouse.
- Visualization/Consumption: With the telemetry data available in Data 360, customers can review system health and gain insights by using pre-built or custom dashboards via Tableau Next. Customers can also leverage the Tableau Concierge, which is a pre-built, agentic analytics skill within Tableau Next, that allows users to ask questions about telemetry data in natural language and receive trusted, actionable answers with visualizations. Customers may also export the data to existing Application Performance Management (APM) systems (for example, DynaTrace, Datadog, Splunk, and so on).
The transition to an Agentic Enterprise is not merely an IT upgrade; it is a fundamental architectural inflection point. A fragmented, siloed deployment of AI agents is a direct path to operational chaos, shadow IT, and unmanageable technical debt. The only sustainable path forward is through a unified, composable architecture. By building on the proven foundation of API-led connectivity, the MuleSoft Agent Fabric delivers the 'central nervous system' required to manage this new digital workforce. It provides the critical capabilities for discovery, orchestration, enterprise-grade governance, and end-to-end observability. This is how we move beyond AI experimentation and begin to architect a truly intelligent, automated, and secure enterprise, transforming autonomous potential into tangible, governed business outcomes.
- Getting Started with Anypoint Code Builder
- Technical Guide to Einstein for Anypoint Code Builder: Generative Flows
- DataWeave Generative Transformation Deep Dive: AI Innovation for Rapid Data Transformation
- Creating API Specs with MuleSoft Dev Agent
- Generating API Documentation With Einstein Generative AI
- MuleSoft MCP Server Overview
- MuleSoft MCP Server Tools
- MCP Connector
- A2A Connector
- Get Started with Agent Fabric
- Securing Agent Interactions with Flex Gateway
- Flex Gateway Agent Policies
- Flex Gateway Policy Development Kit (PDK) Overview
- MuleSoft API Catalog for Salesforce
- Enabling an API Project for Topics and Agent Actions
- Work with Tableau Next
- OpenTelemetry
- Model Context Protocol
- Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol
Nikhil Aggarwal is a Principal Architect at Salesforce, where he leads architecture for MuleSoft and Salesforce Automation Clouds. Nikhil brings over 18 years of experience delivering large-scale products and is passionate about scalable architecture, intuitive developer experiences, and building high-performing teams. Prior to Salesforce, he led multiple initiatives in Microsoft Power Platform, Dataverse and Office 365 from concept to launch. His work continues to shape how modern enterprises connect systems, automate workflows, and unlock business value in the AI-first era.